In this blog, we will explore the key differences between SWITCH and IF functions in DAX. When working with Power BI, both functions help apply conditional logic, but they serve different purposes and impact performance differently.
The IF function is ideal for simple conditions, while SWITCH is more efficient when dealing with multiple conditions. We will also discuss their use cases and when to use each for optimal performance in Power BI.
Key Differences Between SWITCH and IF
| Feature | IF Function | SWITCH Function |
| Purpose | Checks a condition and returns one of two results (TRUE or FALSE). | Compares a value against multiple options and returns a matching result. |
| Complexity | Best for simple TRUE/FALSE conditions. | Best for handling multiple conditions (similar to CASE in SQL). |
| Performance | Slower when dealing with many conditions (nested IFs). | Faster and easier to manage for multiple conditions. |
| Readability | Becomes complex and harder to read with many conditions. | More structured and easier to understand. |
| Alternative to | Excel’s IF function. | SQL’s CASE statement. |
When to Use SWITCH vs. IF?
| Scenario | IF Function | SWITCH Function |
|---|---|---|
| Basic condition check (TRUE/FALSE) | ✅ Best Choice | ❌ Not Needed |
| Handling multiple conditions (3+ cases) | ❌ Hard to manage | ✅ Best Choice |
| Grouping or categorizing data | ❌ Less efficient | ✅ Best Choice |
| Performance with large datasets | ❌ Can slow down | ✅ More optimized |
Example:
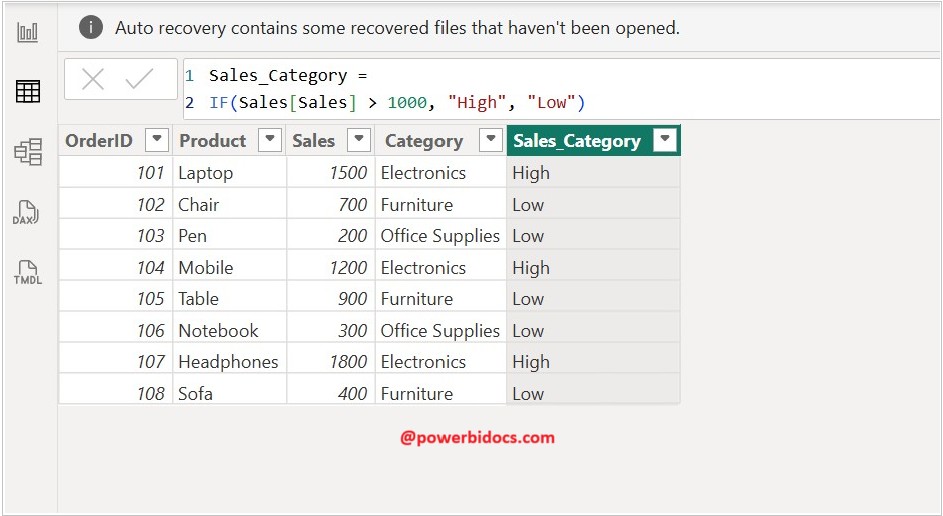
Scenario IF DAX: Classify sales transactions as ‘High’ or ‘Low’ based on a threshold of 1,000.
Sales_Category = IF(Sales[Sales] > 1000, "High", "Low")
Scenario SWITCH DAX: Assign custom labels to product categories.
- Electronics → “Tech”
- Furniture → “Home”
- Office Supplies → “Stationery”
- Any other category → “Other”
Category_Label = SWITCH( Sales[Category], "Electronics", "Tech", "Furniture", "Home", "Office Supplies", "Stationery", "Other" )

Summary
- Use IF for simple TRUE/FALSE conditions.
- Use SWITCH for multiple conditions to improve readability and performance.
- SWITCH is more efficient than using multiple nested IF statements.
- Both functions are useful for conditional formatting, calculated columns, and measures in Power BI.
Thanks for reading this post! I hope you found it helpful. Feel free to share it with others or your teammates so they can benefit from it too. 😊
![]()
